Gihan Fernando
Managing Director / CEO Unique_Infotech_Solutions
Unique Solution for Document Signing with Blockchain Security
The procedure of signing a document is essential because it ensures the creation of legally enforceable responsibilities between the signing parties. Have all the parties signed the sales contract, which appears to be legitimate? Is it the most recent, reviewed version? Can it be demonstrated that the document was unaltered when you signed it? Is it feasible to demonstrate that the document you got matches the one you previously viewed? Despite the fact that many online document signing services offer safe electronic signatures, they are not the same as digital signatures. A handwritten signature may be digitized and used as an electronic signature, but a digital signature verifies its authenticity using mathematical techniques and algorithms. There are currently several digital signature services available that may be used to sign legal documents. All of these solutions for document signing enable users to securely sign documents and also offer cloud storage for the signed papers. Since you must blindly trust a third party to store your papers, these services are more appealing to businesses than to regular consumers. With Blockchain Document Signing, neither the timestamping nor the keeping of signatures require blind faith in outside parties. By creating a blockchain document signing platform, it may be feasible to do away with a third party, and stop people from going back and tracking documents in the event of manipulation or disputes.
The following article will help to understand how blockchain technology has affected the process of document signing.
Let’s first talk about the problems with the present system and why the blockchain is necessary to change it.
Challenges with the current document signature systems
Richly styled documents may be shared with businesses or individuals via PDFs. As security measures were implemented to PDF files by Adobe and other businesses in 2008, it became the industry standard. The PDF’s security features included encryption, digital signatures, and password protection. PDF now has digital signatures to prove who encrypted it and who authored it. It is not difficult to compromise the security of the PDF files, depending on the hashgraph algorithm that is utilized. The document’s content and date/time stamp can be changed.The idea of an ID-tuple, which contains timestamps for when the file was changed and generated, is included in the PDF standard.
However, the protection only covers the whole document and not each individual portion. Let’s say that a paper needs to be signed by several individuals. There is no guarantee as to who amended the document, when, and in what order because not all certificate authorities save their private keys with the same vigilance. Digital documents should be signed sequentially, one at a time. However, the PDF standard does not support several persons signing a document simultaneously and then combining it.
Why Use Blockchain for Document Signing?
With the use of blockchain technology, it is possible to link a collection of documents known as blocks into a chain that is secure and encrypted against hacking. Every block in a blockchain system has a hash, which is like a fingerprint. A hash is created for each block that is added to the chain. Any block manipulation will modify the hash address. All blocks that included the prior hash were rendered invalid as a result.Let’s now examine how blockchain fits into document signing. For the original PDF file, a hash value is calculated and recorded on the blockchain. By comparing the hash of their version with the hash of the original version recorded in the blockchain, authorized parties may confirm that copies of the document are authentic. Parties can use the blockchain document signing platform to check the timestamps associated with the document’s metadata in the case of multiple copies with various signatures. The identity of the signer and an exact time stamp/date may both be stored using blockchain technology. As a result, it may be feasible for many parties to sign a document using a secure and binding legal process.
Here is an example of how the Blockchain Document Signing Platform may operate.
Parties involved in the blockchain document signing ecosystem include the following stakeholders:
Users: To use the site to manage and sign contracts.
Administrator: To examine analytics and user reports.
#1 Register users in the platform
Users sign up for the platform if they wish to utilize it for document signing on the blockchain or to have several parties sign the same document. When enrolling on the platform, they must supply a government-approved form of identification. To validate the people signing the document, a hash matching the identification information is kept on the blockchain.Users don’t need to involve outside parties to utilize the platform for document signing after they’ve registered; they may log in and start using it right away.
#2 The document is uploaded by users to the site.
The document that has to be signed by the signer can be uploaded by users to the site.DOC and PDF files can be submitted as documents.In order to handle the files and keep the record in the blockchain, they may also store the signed papers. Every document that a user submits to the platform would be hashed and preserved, guaranteeing who uploaded the document, when it was posted, and who signed it.
#3 The receivers who must sign papers are added by users.
All signatories (recipients) who will sign the documents can be added by users. They are free to add as many signers as they choose. Signers would receive a signature request in their emails, and to use the platform for document signing, they would need to input their email addresses and a verification number they had just received. Users receive a notice after the document is signed, and the blockchain records the signing-related transaction. When signing a document, signers have the option of using their own handwriting or the government-approved signature method. Transactions stored for document signing would keep track of signature history data that cannot be changed or deleted. Additionally, users can include recipients of the papers as Cc in their emails.
The document is signed by users who provide the signature.
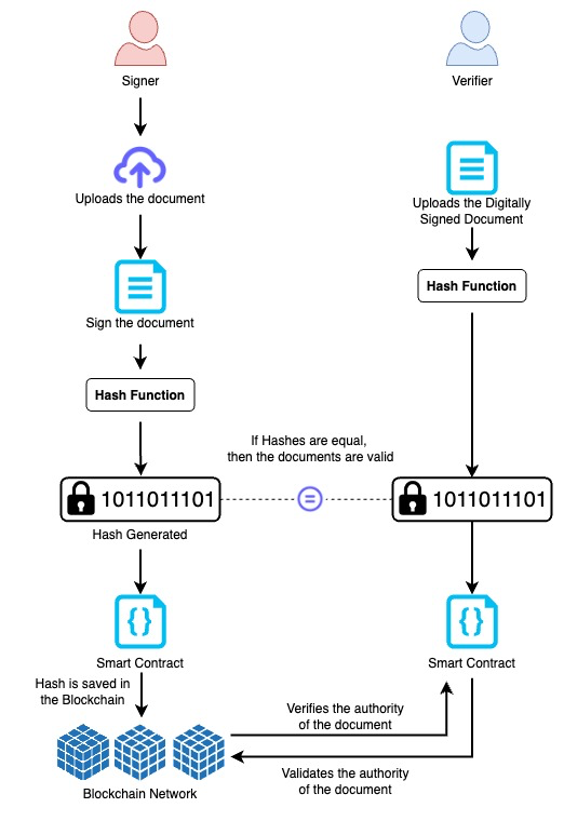
Users who need papers signed or signers who must sign them can either add a legally valid signature to the platform or design their own signature to make a signature. To guarantee the integrity of the signature, each time a user produces or alters the signature, the transaction is stored on the blockchain. It is possible to guarantee that the records saved are immutable and traceable by using the blockchain as a backend component. The signing records can therefore be used to resolve disagreements or conflicts at any moment.
#5 Validation and Authentication of Documents
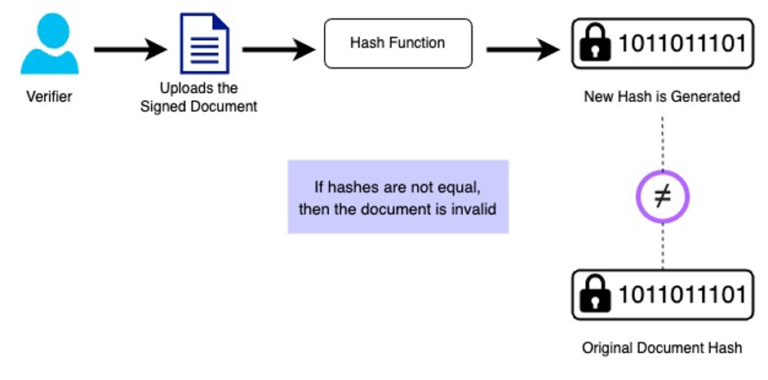
A hash is produced on the blockchain once all parties have signed the document. Any user who has a signed document can utilize the platform to verify its legitimacy. On the blockchain platform for document signing, users can upload the signed document. A signed document will be considered legitimate if the hash created at the moment of signing and the hash obtained after uploading the document match. If the hash is different, there may be a probability that the signed document has been altered or manipulated.
Due to the entire decentralization of the blockchain document signing technology, the admin’s function may be restricted to overseeing user subscriptions and analytics reporting.
On-chain and Off-chain entities
Following are the details that would be stored on-chain:
- User ID
- Document
- Document Signatures
- Finalized Document Hash
- User subscription details
Following are the details that would be stored off-chain:
- User information
- Roles
- Notifications
- Document and Document Transaction ID
- Subscriptions Plans
- Invoices
- Transactions
- Logs
The document signing sector has a lot of prospects because to blockchain’s trust and traceability capabilities. No one entity has authority over the blockchain’s proof of signature.
